Atopic dermatitis is a skin disease characterized by extremely itching which lead to redness, swelling, cracking, clear fluid, and scaling.
Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema. Eczema is any skin condition that makes you itch to the extent of causing redness. Atopic dermatitis can occur at any age. It mostly affects infants and young children.
Criteria that make doctors to diagnose the skin condition is dependent on the features of the rashes and clinical history related to it, family history of asthma and/ or hay fever.
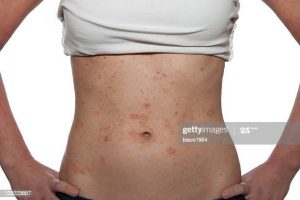
Young girl with Atopic dermatitis, type of eczema. Image credit: Getty Image
SYMPTOMS OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS
In atopic dermatitis, the skin becomes extremely itchy and inflamed, causing redness, swelling, vesicle formation (minute blisters), cracking, weeping, crusting and scaling. This type of eruption is called eczematous. In addition, dry skin is a very common complaint in almost all those afflicted with atopic dermatitis.
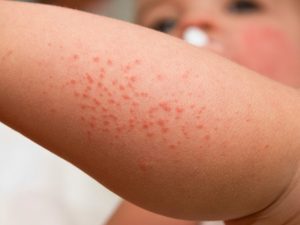 Child with atopic dermatitis. Image Credit: Getty Image
Child with atopic dermatitis. Image Credit: Getty Image
Before the age of 5years, most people have their first signs of eczema. Infants may have red, crusted, scaly areas on their cheeks, scalp or the front of their arms and legs.
Children and adults usually have itchy, red rashes on the back of the neck and knees and in elbow creases. Scratching can lead to infection in which the bumps get filled with pus.

WHAT ARE THE FACTORS THAT CAN TRIGGER ATOPIC DERMATITIS?
- Low humidity
- Seasonal allergies
- Exposure to harsh soap
- Detergents
- Cold weather
TREATMENT
Atopic dermatitis can be persistent. You need to try various treatments over months 0r years to control it. Even if the treatment is successful, signs and symptoms may return.
One or two combination of these drugs can be used to treat Atopic dermatitis:
- Corticosteroids
- Antihistamine
- Drugs that suppress immunity
- Antibiotics to treat infections caused by bacteria.
PREVENTION OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS
Skin care: Sticking with a daily skin care routine can prevent flares. Skin care should include-
- Lukewarm baths to cleanse and moisturize the skin without drying it out.
- Using mild bar soap or non-soap cleanser
- After bath, use creams or ointment. Avoid lotion with high water or alcohol content.
Stay away from any material to which you are allergic eg dust, carpet, rug, wash sheet, molds, pollen, cat or dog dander, certain foods such as eggs, peanuts, milk, fish, soy products or wheat.
Relaxation helps reduce the number of flares. Relax well.
Avoid scratching or rubbing.
Keep your child’s fingernails short to help reduce scratching.
WARNING: People with atopic dermatitis should not get the smallpox vaccine. It may cause serious problems called eczema vaccinatum.
REFERENCE
Mayo Clinic
Medicine Net
WebMD
Medscape

Dr. Adeyemo Olusola is a medical graduate of Olabisi Onabanjo University, Ogun State, Nigeria along with certificate in advanced diploma in Principles of Nutrition, Management and Leadership, Dublin and Certificate in Global Health from London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. In addition to his numerous certifications, he is a certified Telemedicine Physician from Harvard Medical School, USA. He is an avid reader of books from different oases of life, expert in data analysis. “So many a time, I have seen people die avoidable death because of lack of knowledge or information, falling victim of fate. There is then a necessity laid on us to help arm our society to the teeth, as a healthy society cannot be detached from an informed one. Hence, there is need for healthgist.net. We hope you will have a wonderful stay on our website.”

