When we come across the term malnutrition, most people associate it with poverty and underprivileged living but that is not always the case. Anybody can be malnourished regardless of your income; malnutrition is purely based on your lifestyle and diet.
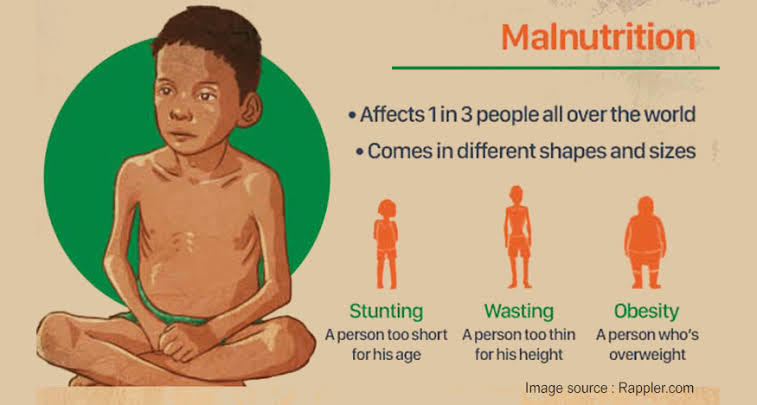
Malnutrition in simple terms is a lack of adequate or excess supply of nutrients needed by the body for proper growth and development. It is a condition that occurs when nutrients are not enough in the diet or when the nutrients are in excess. Malnutrition can lead to several health problems. Depending on the quantity of nutrients you are getting, malnutrition can be classified into overnutrition and undernutrition.
Overnutrition

This is when the nutrients needed for proper growth especially carbohydrates and fats are consumed in excess. A major sign is obesity. In over nutrition, some essential micronutrients may also be lacking. For instance, someone who loves consuming carbohydrate on a daily basis and consumes very little of the other classes of food will be deficient in certain nutrients gotten from those other classes of food. Over nutrition usually leads to obesity which is a risk factor for diabetes and heart diseases, they can also develop micronutrient (e.g. vitamins and minerals) deficiency.
Undernutrition
Undernutrition is another form of malnourishment where the body is not getting adequate nutrients. It could either be as a result of not taking in sufficient nutrients or the inability of one’s body to absorb and utilize nutrients. It results in being underweight and having stunted growth.
Undernutrition can be categorized into undernutrition caused by lack of protein and energy (protein-energy malnutrition) and undernutrition due to dietary deficiencies. Undernutrition could be due to dietary deficiencies in cases whereby the body cannot absorb or utilize nutrients. It could also occur in pregnancy due to the increased nutritional requirements. Protein-energy malnutrition presents in two forms; kwashiorkor (caused by dietary insufficiency of protein with a high carbohydrate diet) and marasmus (loss of body weight and strength due to the lack of dietary calories).
Causes of malnutrition
Malnutrition is primarily caused by an inadequate or excessive supply of nutrients to the body. This could be due to two main factors which are lifestyle and medical conditions.
- Lifestyle
Our lifestyle goes a long way in affecting our health. People with the following lifestyles are at a high risk of malnutrition
– Consuming alcohol excessively. Alcohol can cause a loss of appetite and also inability to absorb needed nutrients
– Sedentary lifestyle
– Inability to get proper diet due to poverty and food scarcity
– Old people that live alone and cannot take care of themselves have a high risk of being malnourished
– Hectic lifestyle
– Making unhealthy food choices
- Health/medical conditions
Some of the following medical conditions can increase the risk of malnutrition;
– Mental conditions such as depression, anorexia nervosa ( an eating disorder characterized by self starvation due to an irrational fear of gaining weight) and bulimia nervosa ( binge eating followed by self induced vomiting)
– Loss of appetite due to illness and certain medications
– Gastrointestinal conditions such as Celiac disease and Crohn’s disease which affects the absorption of certain nutrients
Symptoms of malnutrition
Generally, the symptom of overnutrition is overweight and obesity. Also, the individual may be lacking in certain vitamins and minerals and this can result in low immunity, eye problems and even impaired brain function. Moreover, being overweight and obese can lead to certain health conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure.
Undernutrition on the other hand can present with a variety of symptoms, depending on the severity. These symptoms include;
– Hypoglycemia
– Excessive weight loss
– Stunted growth
– Poor intellectual development (especially in children)
– Constant irritability and nervousness
– Protruding abdomen disproportionate to the body ( in the case of kwashiorkor)
– Hypothermia ( abnormally low body temperature)
You can also know if you are malnourished by your body mass index (BMI). The Federal obesity clinical guidelines define underweight as a BMI of 18 and below, overweight as a BMI of 25-29 and obesity as a BMI of 30 and above. To calculate your BMI, measure your weight (in kilograms) and divide it by the square of your height (in meters).
Prevention
The way to prevent overnutrition is by making healthy food choices. Avoid eating junk food and carbohydrate or sugar-rich fast food. Undernutrition is mostly a consequence of food scarcity due to poverty, war and low income. These people usually need governmental or non-governmental interventions to provide relief materials. If you have easy access to food, in order to prevent undernutrition, make sure you eat healthy, do not skip meals. And if you live a hectic lifestyle, make sure you plan your meals ahead; if you are trying to lose weight, there are exercise and diet plans that can help you on this which are way better and healthier than deliberately starving yourself. Avoid living a sedentary lifestyle; make sure you engage in enough physical exercise. Also increased nutritional demands in children, pregnant women and lactating mothers puts them at a high risk of being malnourished so their diets should always contain adequate nutrients in the right proportion
Treatment
Before a treatment plan is made, your doctor will want to know the cause of your malnutrition and if you have any underlying health conditions. Also treatment will depend on the severity of Malnutrition. In mild cases, a dietician might help you with a dietary plan and therapy. But in severe cases the individual would need to be admitted into the hospital. In severe undernutrition, treatment is aimed at rehydrating the patient, increasing the energy levels by increasing blood sugar and calories, increasing the body temperature from a result of hypothermia and supplying the nutrients that are deficient. After the patient is then stable, a diet plan will be created.
In severe cases of overnutrition, specific tests would be carried out to know which nutrients you might be lacking. In severe obesity, surgery might be needed to remove excess fat and then a dietician will help with a dietary and weight loss plan.

Oyewole Ibukun is currently a Medical student of Olabisi Onabanjo University. She has a passion for seeking knowledge with a creative, detail oriented and analytical mindset.

