Picture of a woman infected with sore throat.
Image credit: google image
Sore throat is a symptom that presents as a pain at the back of your mouth with or without swallowing. The pain comes from various parts of the throat. This include your soft palate, lingual tonsil, tongue, palatine tonsil etc.
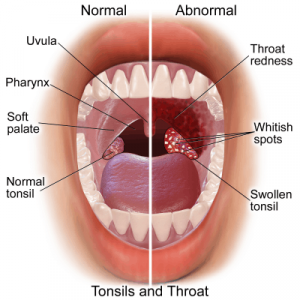
Picture showing normal and infected throat. Image credit: google image
Causes of sore throat include:
- Drugs: Some antihistamine like loratadine reduces mucus secretion causing your throat to be dry resulting in sore throat.
- Chewing tobacco, drinking alcohol and eating spicy food can irritate your throat and result in sore throat.
- Infection: When micro-organisms invade your throat, it causes oedema (swelling) and hyperemia of the mucus membrane. This as well affect your nasal cavity (nose) and eustachian tubes (relating to ear and throat). This can occur in acute pharyngitis, tonsillitis, epiglottitis, and diphtheria.
PHARYNGITIS- A CAUSE OF SORE THROAT
It is the infection or irritation of the throat- Pharynx. Most time, it is viral in origin but sometimes caused by bacterial and fungal. Most of the bacterial cases are related to Group A streptococci (GAS).
CLINICAL FEATURES
Symptoms of pharyngitis include sore throat, fever, difficulty in swallowing, joint pain, muscle aches, and cervical lymphadenopathy.
Pharyngitis of fungal cause is often associated with oral thrush.
Pharyngitis of viral origin is often associated with preceding history of cough or catarrh. Those of adenovirus origin are associated with conjunctivitis while severe icterus is seen in Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV).
When pharyngitis is bacterial in origin with Group A Streptococci (GAS), it is often characterized with
- Sudden onset
- Headache
- Fever
- Tonsillar exudates
- Absence of cough
- Vomiting
- Anterior cervical lymphadenopathy
Watch the video below for other information you need on Sore throat caused by Group A Streptococci (GAS):
Other bacterial cause are Corynebacterium hemolyticus, Mycobacterium pneumoniae, and Corynebacterium diphtheria.
INVESTIGATION
Your doctor may require that you do the following investigations: –
- Complete or full blood count: Your blood count may be normal in case of viral pharyngitis while neutrophilic leukocytosis is seen if your pharyngitis is bacteria in origin.
- Throat culture: This is the gold standard investigation for diagnosing pharyngitis of Group A Streptococci, GAS origin.
- Chest X-ray: This is to exclude pneumonia which is a possible complication of pharyngitis.
TREATMENT
- Ensure adequate hydration status to prevent dehydration.
- Use of oral analgesics and antipyretics.
- When pharyngitis of bacterial origin or cause is clinically suspected and cultured, use of ANTI-BIOTIC within nine (9) days of onset of pharyngitis helps to prevent rheumatic fever (complication of Group A Streptococci, GAS dependent pharyngitis).
- Adequate bed rest.
- Salt water gargle several times a day may help relieve the symptoms
FURTHER READING:
Pathophysiology of clinical symptoms, signs and laboratory parameters by Kanu E. O. Nkanginieme et al..
Medscape
Explain Medicine
Video Credit: Medical Centric

Dr. Adeyemo Olusola is a medical graduate of Olabisi Onabanjo University, Ogun State, Nigeria along with certificate in advanced diploma in Principles of Nutrition, Management and Leadership, Dublin and Certificate in Global Health from London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. In addition to his numerous certifications, he is a certified Telemedicine Physician from Harvard Medical School, USA. He is an avid reader of books from different oases of life, expert in data analysis. “So many a time, I have seen people die avoidable death because of lack of knowledge or information, falling victim of fate. There is then a necessity laid on us to help arm our society to the teeth, as a healthy society cannot be detached from an informed one. Hence, there is need for healthgist.net. We hope you will have a wonderful stay on our website.”