It is a malignant tumour of the pigment of skin. If treated early, the prognosis is often good. Melanoma happens when the skin pigment cells (melanocyte) become cancerous and multiply in an uncontrolled way. They can invade the surrounding skin and metastasized to lymph nodes, liver and lungs.
RISK FACTORS OF MELANOMA
The most important risk factor is exposure to too much ultraviolet light in sunlight.
Fair-skinned people.
Positive family history of melanoma
People who already had one melanoma are at the risk of having another.
People with many (more than 50) ordinary moles, or with a very large dark hairy birthmark, have a higher than average chance of getting melanoma.
SYMPTOMS OF MELANOMA
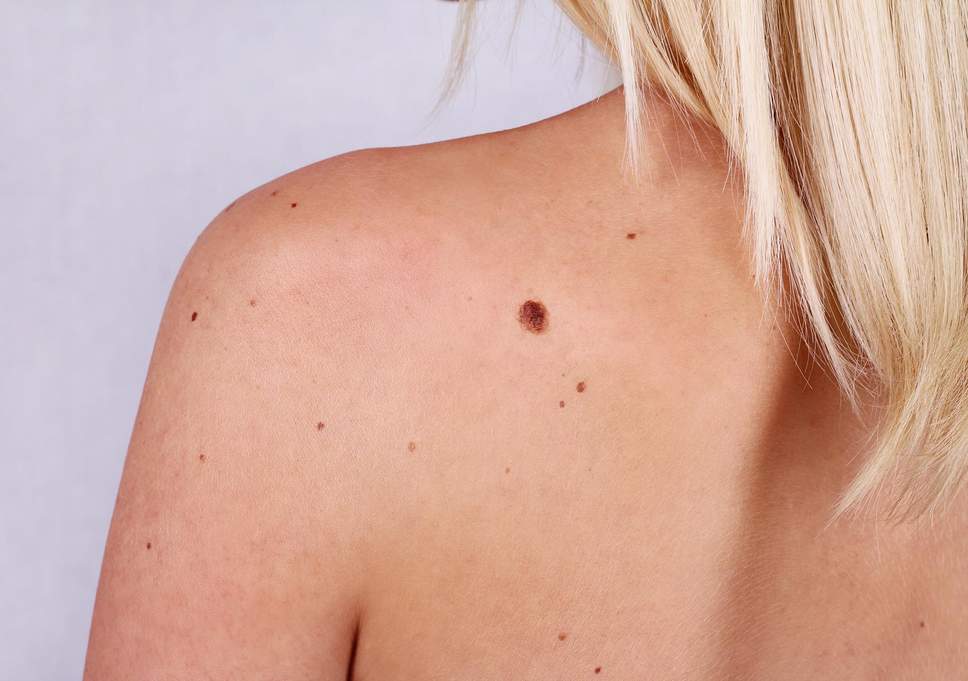
Melanomas usually do not have any symptom but tingling and itching may occur at an early stage. ABCD system tells you some of the things to look out for:
Asymmetry– The two halves of the area differ in their shape.
Border– Border with irregular edges
Colour– Colour variation: Different shades of black, brown and pink may be seen
Diameter– Diameter is greater than 6mm.
There are four types of melanoma. They are classified according to growth pattern as follows:
Superficial spreading melanoma
Nodular melanoma
Lentigo maligna melanoma: It is a type of invasive skin cancer. It develops from lentigo maligna otherwise called Hutchinson’s melanotic freckles. Lentigo maligna grows on the superficial skin layer. When it grows beneath the skin surface, it becomes lentigo malignant melanoma.
Acral lentiginous melanoma
AMERICAN JOINT COMMITTEE ON CANCER (AJCC) STAGING OF MELANOMA
Stage 0: Melanoma only involves the epidermis but has not spread to dermis.
Treatment: 0.5-1cm excision margin is adequate. No other therapy is required except for regular observation for recurrence.
Stage 1: The melanoma is less than 1mm in thickness and is not ulcerated but just localised in the skin.
Treatment: 1cm excision margins are adequate; if lesion is greater than 1mm, 2cm margin is required.
Stage 2: The melanoma is 1.01-2 mm and is not ulcerated and still localized in the skin
Treatment: 2cm margin surgical resection is required.
Stage 3: The melanoma has spread to lymph nodes near the affected skin area. No distant spread is present.
Treatment: 2cm margin and regional lymph node dissection is required.
Stage 4: The melanoma has spread beyond the original area of skin and nearby lymph nodes to other organs in the body.
Treatment: This requires chemotherapy provided that the performance status of the patient is adequate.

Dr. Adeyemo Olusola is a medical graduate of Olabisi Onabanjo University, Ogun State, Nigeria along with certificate in advanced diploma in Principles of Nutrition, Management and Leadership, Dublin and Certificate in Global Health from London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. In addition to his numerous certifications, he is a certified Telemedicine Physician from Harvard Medical School, USA. He is an avid reader of books from different oases of life, expert in data analysis. “So many a time, I have seen people die avoidable death because of lack of knowledge or information, falling victim of fate. There is then a necessity laid on us to help arm our society to the teeth, as a healthy society cannot be detached from an informed one. Hence, there is need for healthgist.net. We hope you will have a wonderful stay on our website.”