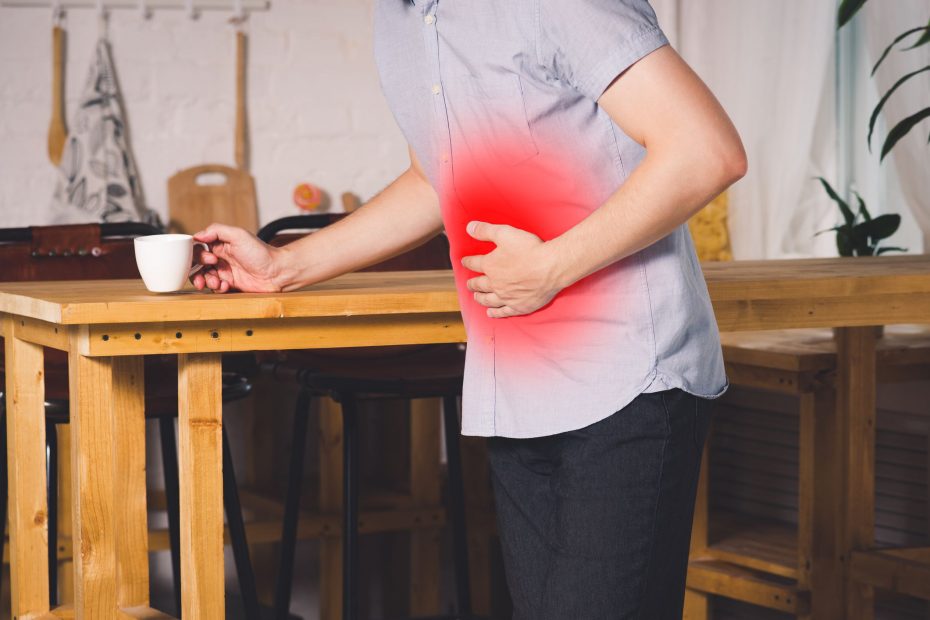
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) refers to an eroded area of the stomach or duodenal mucosa (inner layer) bathed in hydrochloric acid and pepsin which comprise the gastric juice. There is another term called erosion which is not as deep as an ulcer.
The site of the ulcer may perforate (the ulcer on the inner layer of the stomach/duodenum can extend and involve the whole wall causing a hole in the wall) or bleed.
A bacterium known as Helicobacter pylori (H. Pylori) has been implicated as a causative agent of peptic ulcer. Peptic ulcer has other less common causes however; the content of the stomach is acidic and so the stomach and duodenal mucosa have special factors that protect them from this acid such as mucus, bicarbonate, blood flow and prostaglandins; factors that stop these protective mechanisms from working properly can predispose to the development of ulcers. NSAIDS (Non-steroids Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) such as diclofenac, ibuprofen and so on reduce the production of prostaglandins and so prolonged use can cause ulcers.
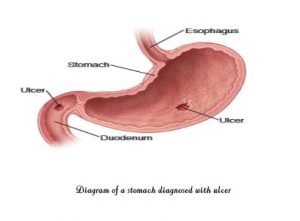
* Ulcer in the duodenum is known as Duodenal ulcer.
* Ulcer in the stomach is called Gastric ulcer.
Pain in the chest or upper abdomen is the most common symptom, others include
– Heartburn
– Indigestion
– Nausea
– Dark coloured stool
– Abdominal discomfort
Diagnosis of PUD
Endoscopy (Putting a long tube with an attached micro camera down your throat to visualize the ulcer) is the gold standard.
There are special tests to confirm the presence H.pylori that include stool and blood tests, urea breath test and biopsy.
Treatment of PUD
A. Drugs that neutralize already secreted acid / coat the ulcer to protect it from stomach acid (ANTACID) e.g. Aluminum hydroxide, calcium carbonate, magnesium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate and Sucralfate.
B. Drugs that reduce acid secretion
1. H2 blockers e.g. Cimetidine, Ranitidine and Famotidine
2. Proton pump inhibitors, i.e. Omeprazole and Lansoprazole
3. Anticholinergics i.e. Pirenzepine
4. Somatostatin, i.e. Octreotide.
C. Drugs that enhance the defense mechanisms
1. Prostaglandins, i.e. Misoprostol
2. Mucus secretion stimulants, i.e. Carbenoxolone
D. Anti H. pylori antibiotics
WARNING: SELF-MEDICATION IS DANGEROUS. SEEK THE OPINION OF YOUR DOCTOR.
Image credits:
1. Wikipedia
2. Fairview.org

Pharm. Fatima Ajide J. is a current pharmacology student at Olabisi Onabanjo University.
She has a passion in researching about the interaction between organs and drugs (i. e. the Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetics).
A practicing Muslim and hobbies are tourism, reading and Research.

