One of the most worrisome periods of a person with a Non-AA Genotype is when they intend to start a serious relationship with the intent of marriage. They sometimes find it very difficult to ask for the Genotype of their proposed spouse, despite reasonable knowledge of the challenges involved with a mismatch. This difficulty is usually due to the fear of the unknown, ‘what if we are not compatible?’, ‘I dont want to leave him’, ‘I really like him’, ‘We will talk about it later’ and other reasons best known.
This is why many couples today only get to know their genotypes during premarital counselling, as most institutions, religious groups or otherwise require the results of this very crucial investigation. If they happen not to be a match, one of these two things usually happen. They could decide to end things with a lot of regret about how much time they have wasted while some couples decide to roll the dice and still get married.

I once had a patient who had a sickle cell crisis and was admitted for expert care. The kid was a lovable child and it was very emotional to see him in so much pain. As if that was not enough, they had 3 children with sickle cell disease. So, I asked the parents to know if they never had the brainwave of their genotype mismatch before tying the knot. To my surprise, she said she was aware but was misinformed during counseling. She and her husband were both AS. They were informed that there was a 1 out of 4 chance that each of their children would have the disease. With this, they assumed it meant that they would have 3 healthy children out of 4. Unbeknownst to them, the 25% probability is per child so a couple that are both AS can have 10 children that are healthy, or 10 children that are all sick. She really wished she could go back in time to reverse the pain of the children and lengthen their life expectancy.
Sickle cell disease is a group of red blood cell disorders that affects hemoglobin which delivers oxygen to cells throughout the body. Individuals with this disorder have an abnormal hemoglobin molecule called hemoglobin S, which distorts the red blood cell shape into a sickle or crescent shape.
Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene, one from each parent.
Other subtypes exist, depending on the mutations in each haemoglobin gene but they are not as common as the S mutation.
Sickle cell disease patients frequently get painful attacks called vasoocclusive crises. It can be set off by temperature changes, stress, dehydration, illness and high altitude to mention a few.
A person with a single abnormal copy does not usually have symptoms and is said to have sickle cell trait and is referred to as a CARRIER. A person with 2 abnormal genes is however said to have sickle cell disease or sickle cell anemia. Our interest is then focused on this particular group.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS·
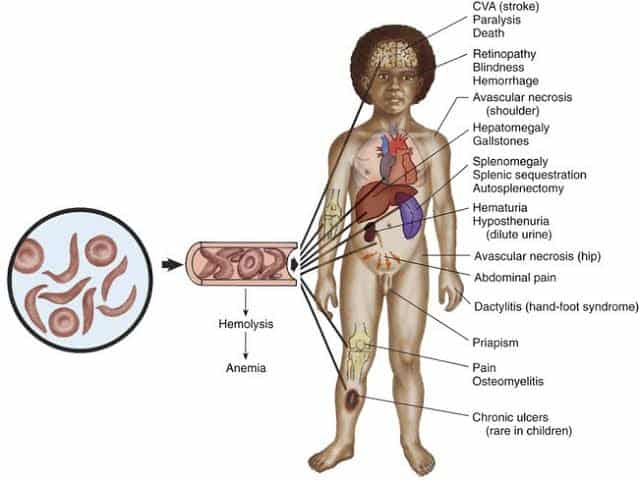
Anaemia: This results from the premature break down of the abnormally-shaped cells, thereby reducing the amount of Red cells available for Oxygenation of the body organs. This can be easily noticed by paleness of parts of the body.·
Bone pains with earliest manifestation as hand and foot syndrome: This Usually manifests after age 1, when there is reduced production of fetal hemoglobins and increasedproduction of the abnormal hemoglobins. These hemoglobins on sickling occlude the end arteries with resultant pain due to reduced blood supply to the affected area·
Jaundice: Excessive breakdown of the RbCs has an end product of bilirubin which in large quantity and reduced excretion causes yellowness of the skin and eyes·
Difficulty in breathing
Easy fatiguability
Delayed growth and development in children.
Diagnosis is by a simple blood test.
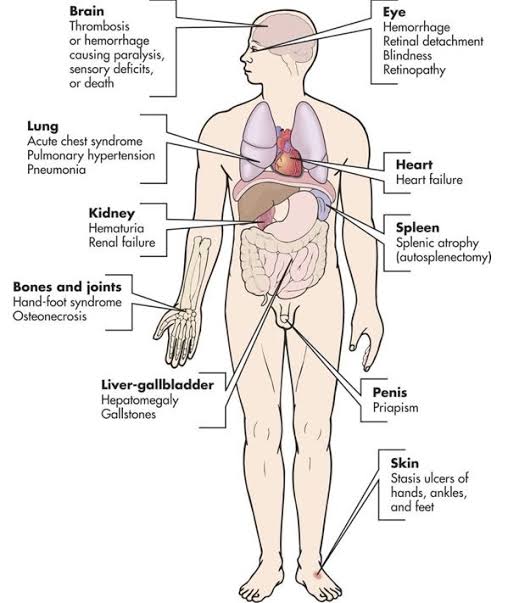
COMPLICATIONS
·Chronic pain
·Stroke
·Avascular bone necrosis
·Ulcers
·Priapism (prolonged painful penile erection)
·Pulmonary hypertension
·Vision problems·
.End organ failures : These repeated end arteries occlusion deprive tissues and organs of oxygen-rich blood and can lead to organ damage, especially in the lungs, kidneys, spleen and brain.
A particularly serious complication of sickle cell disease is high blood pressure in the blood vessels that supply the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Pulmonary hypertension occurs in about one-third of adults with sickle cell disease and can lead to heart failure.
Sickle cell disease patients also frequently take certain medications and they can suffer side effects and toxicity of these drugs.
Know your genotype and your prospective partner’s genotype today.
GENOTYPE COMPATIBILITY TEST
Study this table below carefully:
AA + AA = AA, AA, AA, AA (Excellent)
AA + AS = AA, AS, AA, AS (Good)
AA + SS = AS, AS, AS, AS (Fair)
AA + AC = AA, AA, AA, AC (Good)
AS + AS = AA, AS, AS, SS (Very Bad)
AS + SS = AS, SS, SS, SS (Very Bad)
AS + AC = AA, AC, AS, SC (Bad; Advice needed)
SS + SS = SS, SS, SS, SS (Very Bad)
AC + SS = AS, AS, SC, SC (Very Bad)
AC + AC = AA, AC, AC, CC ( Very Bad)
Be bold with your decisions, be firm with the truth. Healing doesn’t mean the damage never existed, it simply means you are not controlled by that circumstance. Take charge!
Do not take the decision to cheat yourself, your best time to ask the question is when it pops up in your head. Don’t procrastinate or feel weak💥
Thank you for reading!

Dr Oluwafemi B. Adesina hails from Ogun State, Nigeria and lives in Abuja.
He gained admission to Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta in 2007 but left before the end of the program to badge an M.B.Ch.B. degree from Olabisi Onabanjo University.
He has passion for counseling, coupled with his undying love for human psychology.
He is popularly known as Obawinsome/Professor-X due to his is vast knowledge in sexual therapy. He has several awards and recognitions crowning his Leadership Qualities.
He is quite open minded with a vast use of sarcasm!
